The second generation of mobile communications is the most widely used in Russian Federation. That generation is presented with GSM 900/1800 and CDMA 450 standards. Both of those standards are used for voice calls, text messages and mobile internet access, though it is not that fast as 3G and far more slower that 4G network that works in some regions of Russia. Major providers here are MegaFon, MTS, Beeline, VympelCom and Tele2. The average coverage compiles up to 85% of country's territory. But we should mention that MTS has a 100% coverage over the all Russian Federation.
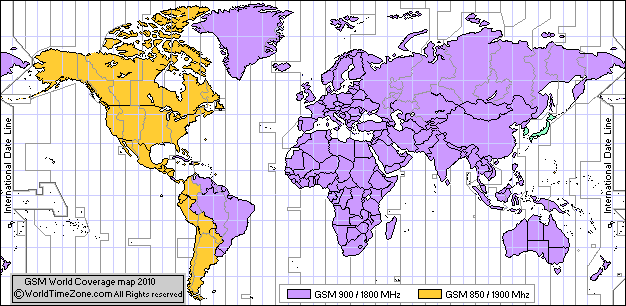
(GSM Coverage World Map)
GSM standard in Russia uses 900 and 1800 MHz frequencies. As long as all mobile phones are duplex devices they use two frequencies simultaneously, one for receiving and one for sending information. Network based positioning or cell tower triangulation uses exactly those frequencies. CDMA works at around 463-467 MHz and 2000-2100 MHz. As it was already mentioned – those standards are used for text messages and voice calls. GPRS and EDGE mobile Internet technology also uses those frequency bands. You can view the full frequency chart of Russian mobile communications below.
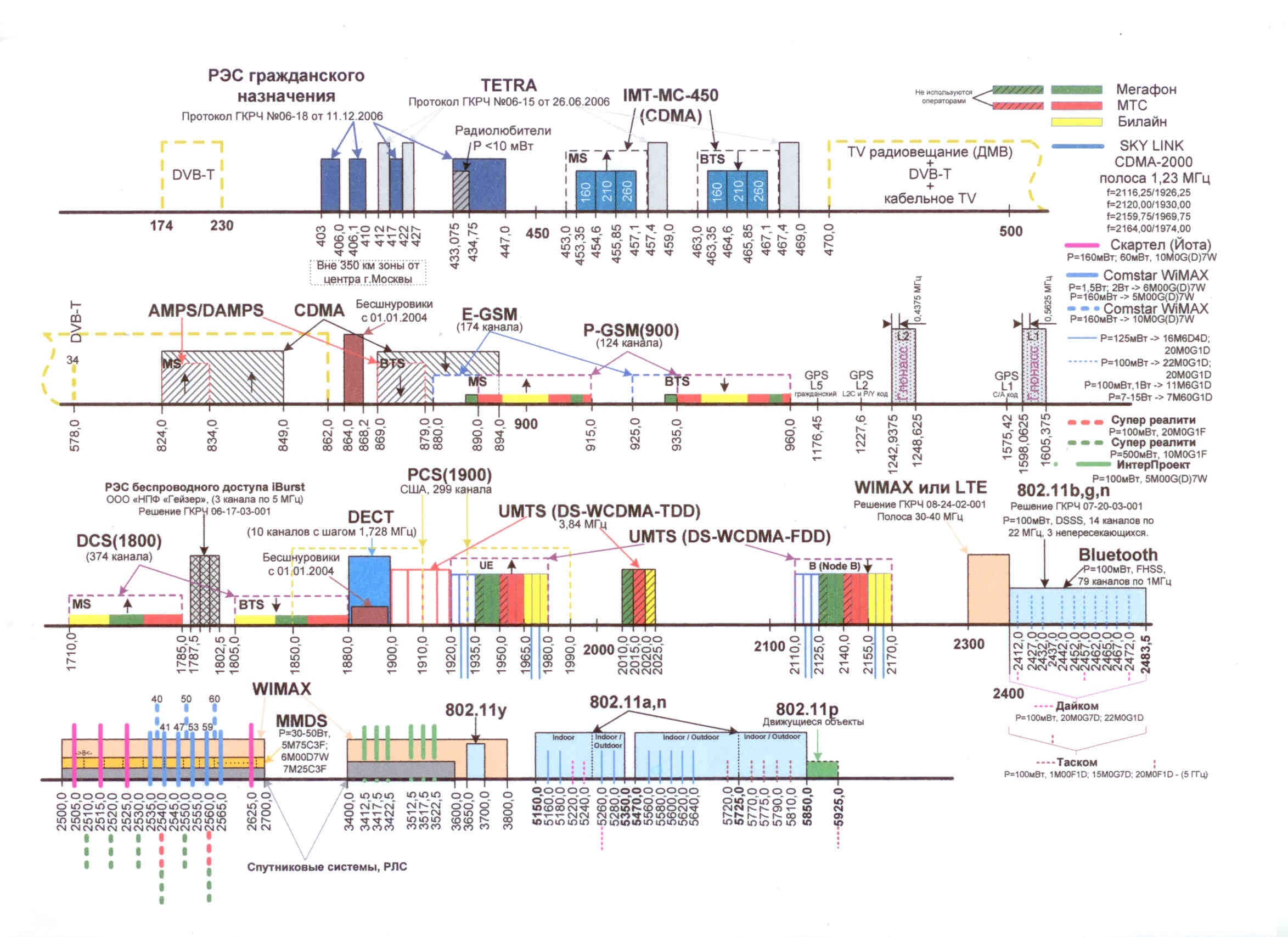 (Russian Frequency Allocation Chart)
(Russian Frequency Allocation Chart)
Third generation of mobile communications, which are widely used all over the world are used in Russian Federation too. Those networks are working at a very high frequency range and the most common radio frequency for those networks is 2000 MHz frequency band. Data transmissions speeds in that generation of mobile communications varies between 2-14 Mbit/s. 3G enables fast mobile Internet access and the possibility to use video calls.
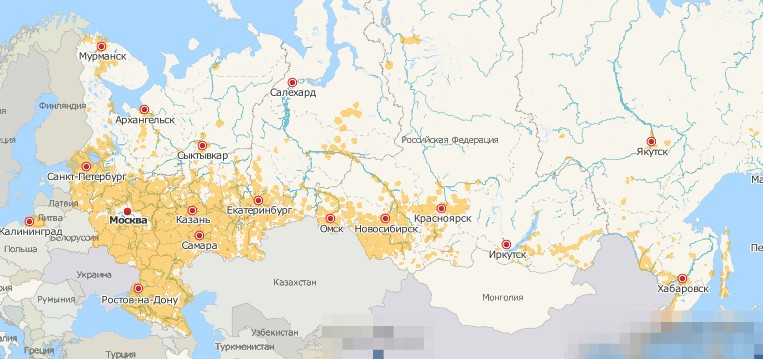
(Beeline 3G Coverage)
When it comes to Russia we can say that MTS, MegaFon, VympelCom and Beeline are the major carriers and they maintain 3G networks in 120 major cities of Russian Federation. 1935-2170 MHz frequency is used for 3G networks in Russia. The coverage of 3G mobile service is not that big, it is concentrated in densely populated areas.
4G networks were recently presented in Russia too. The first companies that were building those networks were Yota and Freshtel. After those two carriers MTS and MegaFon started to develop their own networks. Russian Federation has its own factory that produces 4G base stations and network equipment. Fourth generation of mobile communications develops really fast in Russia, the first city where the 4G LTE network was launched was Novosibirsk and then Moscow. There are two big frequency bands that were assigned for 4G and they are 791-862 MHz for LTE and 2500-2600 for Wi-Max. 4G LTE works in Moscow, St.Petersburg, Sochi, Samara, Novosibirsk, Ufa and Krasnodar.
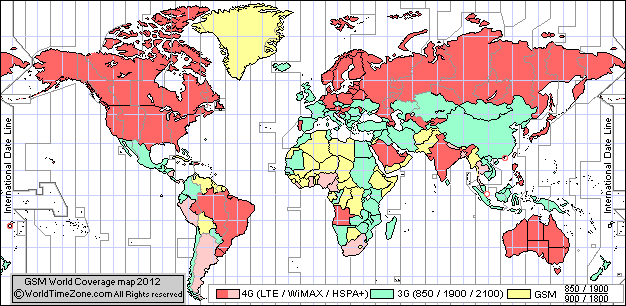
(4G Coverage World Map)
That were the most popular mobile standards in Russia, but we should also mention that they have their own global navigation system that is a worthy substitution to American GPS. That GNSS is called GLONASS and it also has some differences. While GPS works in three channels and uses 1575.42, 1227.60 and 1176.45 MHz frequencies, GLONASS works with 2 channels and its frequencies are 1602-1615 and 1246-1256 MHz. GLONASS satellites have higher orbits and that's the reason why they have better productivity in near-polar regions. Both GPS and GLONASS are frequently used in Russian Federation.
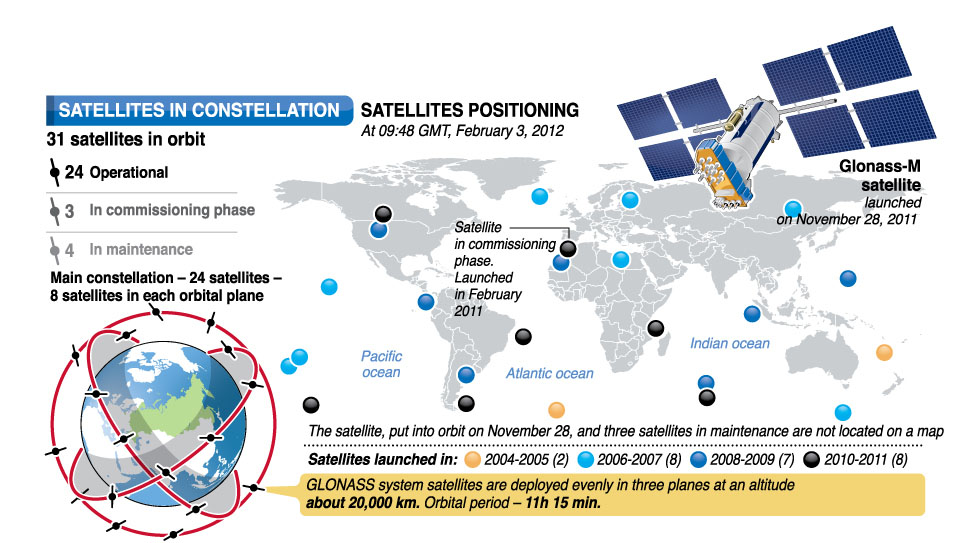
(GLONASS Satellite Constellation Description)
If you are a traveler you should know that biggest mobile carriers in Russia provide a decent roaming services, but if you would like to buy a local SIM card with local phone number you will have to show you papers to the dealer. That's a common procedure in Russia.
Prev : Brazil
Next : Mexico



